Simultaneous Perturbation Stochastic Approximation of the Quantum Fisher Information
1IBM Quantum, IBM Research – Zurich, CH-8803 Rüschlikon, Switzerland
2Institute of Physics, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), CH-1015 Lausanne, Switzerland
3Institute for Theoretical Physics, ETH Zurich, CH-8092 Zürich, Switzerland
| Published: | 2021-10-20, volume 5, page 567 |
| Eprint: | arXiv:2103.09232v2 |
| Doi: | https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2021-10-20-567 |
| Citation: | Quantum 5, 567 (2021). |
Find this paper interesting or want to discuss? Scite or leave a comment on SciRate.
Abstract
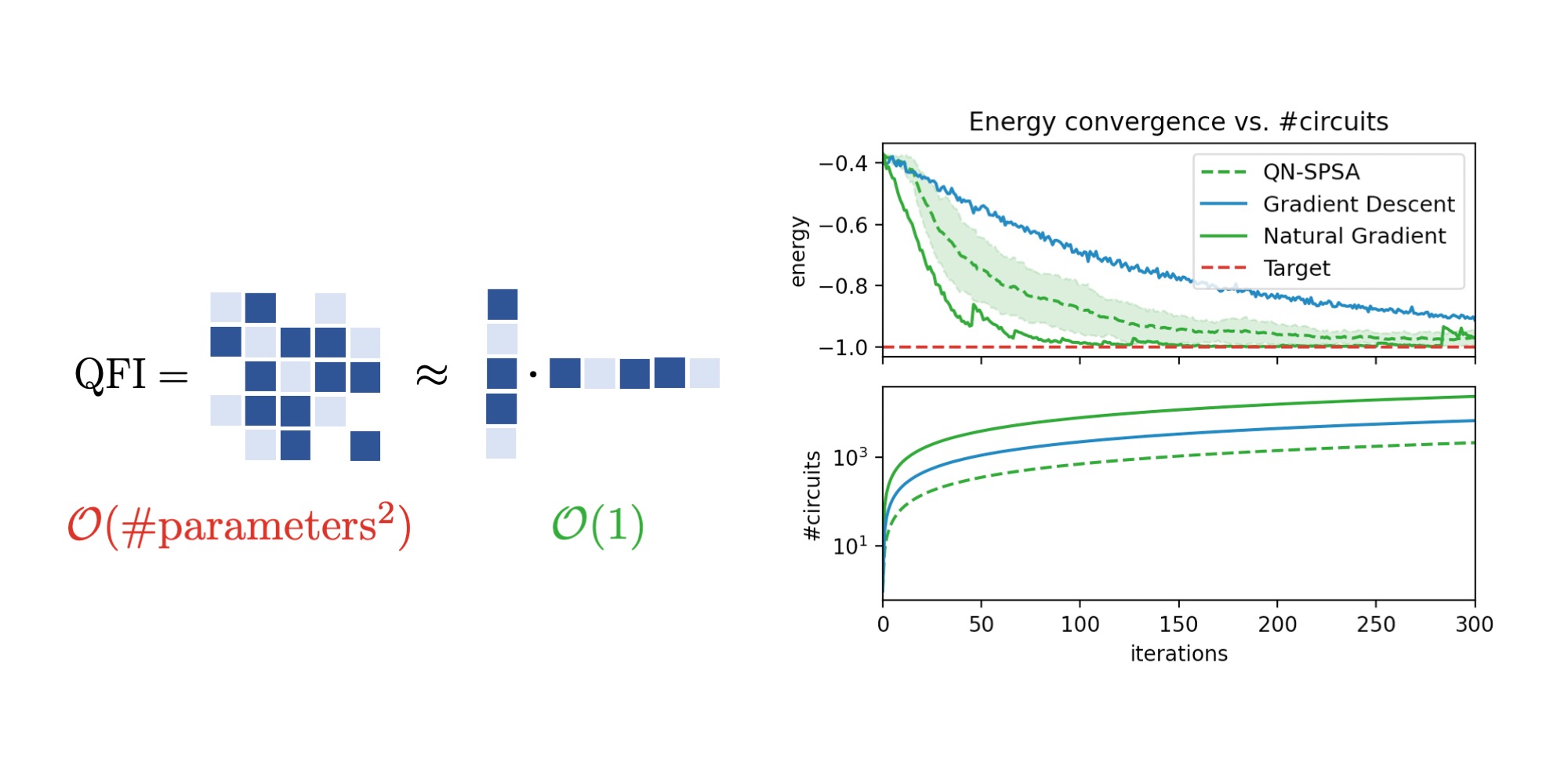
The Quantum Fisher Information matrix (QFIM) is a central metric in promising algorithms, such as Quantum Natural Gradient Descent and Variational Quantum Imaginary Time Evolution. Computing the full QFIM for a model with $d$ parameters, however, is computationally expensive and generally requires $\mathcal{O}(d^2)$ function evaluations. To remedy these increasing costs in high-dimensional parameter spaces, we propose using simultaneous perturbation stochastic approximation techniques to approximate the QFIM at a constant cost. We present the resulting algorithm and successfully apply it to prepare Hamiltonian ground states and train Variational Quantum Boltzmann Machines.
► BibTeX data
► References
[1] Alán Aspuru-Guzik, Anthony D. Dutoi, Peter J. Love, and Martin Head-Gordon. Simulated Quantum Computation of Molecular Energies. Science, 309 (5741): 1704–1707, September 2005. 10.1126/science.1113479.
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1113479
[2] Alberto Peruzzo et al. A variational eigenvalue solver on a photonic quantum processor. Nature Communications, 5: 4213, July 2014. 10.1038/ncomms5213.
https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5213
[3] Mari Carmen Bañuls et al. Simulating lattice gauge theories within quantum technologies. European Physical Journal D, 74 (8): 165, August 2020. 10.1140/epjd/e2020-100571-8.
https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2020-100571-8
[4] Alejandro Perdomo-Ortiz, Neil Dickson, Marshall Drew-Brook, Geordie Rose, and Alán Aspuru-Guzik. Finding low-energy conformations of lattice protein models by quantum annealing. Scientific Reports, 2: 571, August 2012. 10.1038/srep00571.
https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00571
[5] Mark Fingerhuth, Tomáš Babej, and Christopher Ing. A quantum alternating operator ansatz with hard and soft constraints for lattice protein folding. arXiv, October 2018. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.13411.
arXiv:1810.13411
[6] Anton Robert, Panagiotis Kl. Barkoutsos, Stefan Woerner, and Ivano Tavernelli. Resource-efficient quantum algorithm for protein folding. npj Quantum Information, 7 (1): 38, February 2021. ISSN 2056-6387. 10.1038/s41534-021-00368-4.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-021-00368-4
[7] Edward Farhi, Jeffrey Goldstone, and Sam Gutmann. A Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm. arXiv, November 2014. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/1411.4028.
arXiv:1411.4028
[8] Austin Gilliam, Stefan Woerner, and Constantin Gonciulea. Grover Adaptive Search for Constrained Polynomial Binary Optimization. arXiv, December 2019. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.04088. 10.22331/q-2021-04-08-428.
https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2021-04-08-428
arXiv:1912.04088
[9] Lee Braine, Daniel J. Egger, Jennifer Glick, and Stefan Woerner. Quantum Algorithms for Mixed Binary Optimization applied to Transaction Settlement. arXiv, October 2019. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.05788. 10.1109/TQE.2021.3063635.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TQE.2021.3063635
arXiv:1910.05788
[10] J. Gacon, C. Zoufal, and S. Woerner. Quantum-enhanced simulation-based optimization. In 2020 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE), pages 47–55, 2020. 10.1109/QCE49297.2020.00017.
https://doi.org/10.1109/QCE49297.2020.00017
[11] D. J. Egger et al. Quantum computing for finance: State-of-the-art and future prospects. IEEE Transactions on Quantum Engineering, 1: 1–24, 2020. 10.1109/TQE.2020.3030314.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TQE.2020.3030314
[12] J. S. Otterbach et al. Unsupervised Machine Learning on a Hybrid Quantum Computer. arXiv, December 2017. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.05771.
arXiv:1712.05771
[13] Vojtěch Havlíček et al. Supervised learning with quantum-enhanced feature spaces. Nature, 567 (7747): 209–212, March 2019. 10.1038/s41586-019-0980-2.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0980-2
[14] Maria Schuld. Quantum machine learning models are kernel methods. arXiv, January 2021. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.11020.
arXiv:2101.11020
[15] Nikolaj Moll et al. Quantum optimization using variational algorithms on near-term quantum devices. Quantum Science and Technology, 3 (3): 030503, July 2018. 10.1088/2058-9565/aab822.
https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-9565/aab822
[16] Sam McArdle et al. Variational ansatz-based quantum simulation of imaginary time evolution. npj Quantum Information, 5 (1), Sep 2019. ISSN 2056-6387. 10.1038/s41534-019-0187-2.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-019-0187-2
[17] Xiao Yuan, Suguru Endo, Qi Zhao, Ying Li, and Simon C. Benjamin. Theory of variational quantum simulation. Quantum, 3: 191, October 2019. ISSN 2521-327X. 10.22331/q-2019-10-07-191.
https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2019-10-07-191
[18] Christa Zoufal, Aurélien Lucchi, and Stefan Woerner. Variational quantum boltzmann machines. Quantum Machine Intelligence, 3: 7, 2020. ISSN 2524-4914. 10.1007/s42484-020-00033-7.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s42484-020-00033-7
[19] Taku Matsui. Quantum statistical mechanics and Feller semigroup. Quantum Probability Communications, 1998. 10.1142/9789812816054_0004.
https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812816054_0004
[20] Masoud Khalkhali and Matilde Marcolli. An Invitation to Noncommutative Geometry. World Scientific, 2008. 10.1142/6422.
https://doi.org/10.1142/6422
[21] J. Eisert, M. Friesdorf, and C. Gogolin. Quantum many-body systems out of equilibrium. Nature Physics, 11 (2), 2015. 10.1038/nphys3215.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3215
[22] Fernando G. S. L. Brandão et al. Quantum SDP Solvers: Large speed-ups, optimality, and applications to quantum learning. arXiv, 2017. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.02581.
arXiv:1710.02581
[23] Mohammad H. Amin, Evgeny Andriyash, Jason Rolfe, Bohdan Kulchytskyy, and Roger Melko. Quantum Boltzmann Machine. Phys. Rev. X, 8, 2018. 10.1103/PhysRevX.8.021050.
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.8.021050
[24] James Stokes, Josh Izaac, Nathan Killoran, and Giuseppe Carleo. Quantum natural gradient. Quantum, 4: 269, May 2020. ISSN 2521-327X. 10.22331/q-2020-05-25-269.
https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2020-05-25-269
[25] S. Amari and S. C. Douglas. Why natural gradient? In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP '98 (Cat. No.98CH36181), volume 2, pages 1213–1216 vol.2, 1998. 10.1109/ICASSP.1998.675489.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.1998.675489
[26] J.C. Spall. Multivariate stochastic approximation using a simultaneous perturbation gradient approximation. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 37 (3): 332–341, 1992. 10.1109/9.119632.
https://doi.org/10.1109/9.119632
[27] Lingyao Meng and James C. Spall. Efficient computation of the fisher information matrix in the em algorithm. In 2017 51st Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), pages 1–6, 2017. 10.1109/CISS.2017.7926126.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CISS.2017.7926126
[28] A. Cauchy. Methode generale pour la resolution des systemes d'equations simultanees. C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris, 25: 536–538, 1847. 10.1017/cbo9780511702396.063.
https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511702396.063
[29] J. C. Spall. Accelerated second-order stochastic optimization using only function measurements. In Proceedings of the 36th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, volume 2, pages 1417–1424 vol.2, December 1997. 10.1109/CDC.1997.657661. ISSN: 0191-2216.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CDC.1997.657661
[30] Yuan Yao, Pierre Cussenot, Alex Vigneron, and Filippo M. Miatto. Natural Gradient Optimization for Optical Quantum Circuits. arXiv, June 2021. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.13660.
arXiv:2106.13660
[31] Maria Schuld, Ville Bergholm, Christian Gogolin, Josh Izaac, and Nathan Killoran. Evaluating analytic gradients on quantum hardware. Phys. Rev. A, 99 (3): 032331, March 2019. 10.1103/PhysRevA.99.032331.
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.99.032331
[32] Johannes Jakob Meyer. Fisher Information in Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum Applications. Quantum, 5: 539, September 2021. ISSN 2521-327X. 10.22331/q-2021-09-09-539.
https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2021-09-09-539
[33] Andrea Mari, Thomas R. Bromley, and Nathan Killoran. Estimating the gradient and higher-order derivatives on quantum hardware. Phys. Rev. A, 103 (1): 012405, Jan 2021. 10.1103/PhysRevA.103.012405.
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.103.012405
[34] Harry Buhrman, Richard Cleve, John Watrous, and Ronald de Wolf. Quantum fingerprinting. Phys. Rev. Lett., 87 (16): 167902, Sep 2001. 10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.167902.
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.167902
[35] Lukasz Cincio, Yiğit Subaşı, Andrew T. Sornborger, and Patrick J. Coles. Learning the quantum algorithm for state overlap. arXiv, November 2018. URL http://arxiv.org/abs/1803.04114. 10.1088/1367-2630/aae94a.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/aae94a
arXiv:1803.04114
[36] A. Elben, B. Vermersch, C. F. Roos, and P. Zoller. Statistical correlations between locally randomized measurements: A toolbox for probing entanglement in many-body quantum states. Phys. Rev. A, 99 (5), May 2019. 10.1103/PhysRevA.99.052323.
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.99.052323
[37] Kristan Temme, Tobias J. Osborne, Karl Gerd H. Vollbrecht, David Poulin, and Frank Verstraete. Quantum Metropolis Sampling. Nature, 471, 2011. 10.1038/nature09770.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09770
[38] Man-Hong Yung and Alán Aspuru-Guzik. A quantum–quantum Metropolis algorithm. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109 (3), 2012. 10.1073/pnas.1111758109.
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1111758109
[39] David Poulin and Pawel Wocjan. Sampling from the Thermal Quantum Gibbs State and Evaluating Partition Functions with a Quantum Computer. Phys. Rev. Lett., 103 (22), 2009. 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.220502.
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.220502
[40] Mario Motta and et al. Determining eigenstates and thermal states on a quantum computer using quantum imaginary time evolution. Nature Physics, 16 (2), 2020. 10.1038/s41567-019-0704-4.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-019-0704-4
[41] Fernando G. S. L. Brandão and Michael J. Kastoryano. Finite Correlation Length Implies Efficient Preparation of Quantum Thermal States. Communications in Mathematical Physics, 365 (1), 2019. 10.1007/s00220-018-3150-8.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00220-018-3150-8
[42] Michael J. Kastoryano and Fernando G. S. L. Brandão. Quantum Gibbs Samplers: The Commuting Case. Communications in Mathematical Physics, 344 (3), 2016. 10.1007/s00220-016-2641-8.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00220-016-2641-8
[43] Jingxiang Wu and Timothy H. Hsieh. Variational Thermal Quantum Simulation via Thermofield Double States. Phys. Rev. Lett., 123 (22), 2019. 10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.220502.
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.220502
[44] Anirban Chowdhury, Guang Hao Low, and Nathan Wiebe. A Variational Quantum Algorithm for Preparing Quantum Gibbs States. arXiv, 2020. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.00055.
arXiv:2002.00055
[45] A.D. McLachlan. A variational solution of the time-dependent Schrödinger equation. Molecular Physics, 8 (1), 1964. 10.1080/00268976400100041.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00268976400100041
[46] Héctor Abraham et al. Qiskit: An open-source framework for quantum computing. 2019. 10.5281/zenodo.2562110.
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2562110
[47] IBM Quantum, 2021. URL https://quantum-computing.ibm.com/services/docs/services/runtime/.
https://quantum-computing.ibm.com/services/docs/services/runtime/
[48] Sergey Bravyi, Jay M. Gambetta, Antonio Mezzacapo, and Kristan Temme. Tapering off qubits to simulate fermionic hamiltonians. arXiv, 2017. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.08213.
arXiv:1701.08213
[49] Abhinav Kandala et al. Hardware-efficient variational quantum eigensolver for small molecules and quantum magnets. Nature, 549 (7671): 242–246, September 2017. 10.1038/nature23879.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23879
[50] Abhinav Kandala, Kristan Temme, Antonio D. Corcoles, Antonio Mezzacapo, Jerry M. Chow, and Jay M. Gambetta. Error mitigation extends the computational reach of a noisy quantum processor. Nature, 567 (7749): 491–495, March 2019. 10.1038/s41586-019-1040-7.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1040-7
[51] Jonas M. Kübler, Andrew Arrasmith, Lukasz Cincio, and Patrick J. Coles. An Adaptive Optimizer for Measurement-Frugal Variational Algorithms. Quantum, 4: 263, May 2020. ISSN 2521-327X. 10.22331/q-2020-05-11-263.
https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2020-05-11-263
Cited by
[1] Christa Zoufal, David Sutter, and Stefan Woerner, "Error bounds for variational quantum time evolution", Physical Review Applied 20 4, 044059 (2023).
[2] Xinglan Zhang and Feng Zhang, "Variational Quantum Computation Integer Factorization Algorithm", International Journal of Theoretical Physics 62 11, 245 (2023).
[3] Yizhi Wang, Shichuan Xue, Yaxuan Wang, Jiangfang Ding, Weixu Shi, Dongyang Wang, Yong Liu, Yingwen Liu, Xiang Fu, Guangyao Huang, Anqi Huang, Mingtang Deng, and Junjie Wu, "Experimental quantum natural gradient optimization in photonics", Optics Letters 48 14, 3745 (2023).
[4] Daniel Faílde, José Daniel Viqueira, Mariamo Mussa Juane, and Andrés Gómez, "Using Differential Evolution to avoid local minima in Variational Quantum Algorithms", Scientific Reports 13 1, 16230 (2023).
[5] Seokhun Jeon, Yunpyo Hong, and Byung-Soo Kim, 2023 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE) 326 (2023) ISBN:979-8-3503-4323-6.
[6] Julien Gacon, Jannes Nys, Riccardo Rossi, Stefan Woerner, and Giuseppe Carleo, "Variational quantum time evolution without the quantum geometric tensor", Physical Review Research 6 1, 013143 (2024).
[7] Julien Gacon, Christa Zoufal, Giuseppe Carleo, and Stefan Woerner, 2023 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE) 129 (2023) ISBN:979-8-3503-4323-6.
[8] Yaswitha Gujju, Atsushi Matsuo, and Rudy Raymond, "Quantum machine learning on near-term quantum devices: Current state of supervised and unsupervised techniques for real-world applications", Physical Review Applied 21 6, 067001 (2024).
[9] Johannes Weidenfeller, Lucia C. Valor, Julien Gacon, Caroline Tornow, Luciano Bello, Stefan Woerner, and Daniel J. Egger, "Scaling of the quantum approximate optimization algorithm on superconducting qubit based hardware", Quantum 6, 870 (2022).
[10] Joel Bierman, Yingzhou Li, and Jianfeng Lu, "Quantum Orbital Minimization Method for Excited States Calculation on a Quantum Computer", Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 18 8, 4674 (2022).
[11] Nikita Astrakhantsev, Guglielmo Mazzola, Ivano Tavernelli, and Giuseppe Carleo, "Phenomenological theory of variational quantum ground-state preparation", Physical Review Research 5 3, 033225 (2023).
[12] Pauline J Ollitrault, Sven Jandura, Alexander Miessen, Irene Burghardt, Rocco Martinazzo, Francesco Tacchino, and Ivano Tavernelli, "Quantum algorithms for grid-based variational time evolution", Quantum 7, 1139 (2023).
[13] Jules Tilly, Hongxiang Chen, Shuxiang Cao, Dario Picozzi, Kanav Setia, Ying Li, Edward Grant, Leonard Wossnig, Ivan Rungger, George H. Booth, and Jonathan Tennyson, "The Variational Quantum Eigensolver: A review of methods and best practices", Physics Reports 986, 1 (2022).
[14] Antoine Michel, Sebastian Grijalva, Loïc Henriet, Christophe Domain, and Antoine Browaeys, "Blueprint for a digital-analog variational quantum eigensolver using Rydberg atom arrays", Physical Review A 107 4, 042602 (2023).
[15] J. Gidi, B. Candia, A. D. Muñoz-Moller, A. Rojas, L. Pereira, M. Muñoz, L. Zambrano, and A. Delgado, "Stochastic optimization algorithms for quantum applications", Physical Review A 108 3, 032409 (2023).
[16] Nico Meyer, Daniel D. Scherer, Axel Plinge, Christopher Mutschler, and Michael J. Hartmann, 2023 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE) 36 (2023) ISBN:979-8-3503-4323-6.
[17] Gabriele Agliardi and Enrico Prati, "Optimal Tuning of Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks for Multivariate Distribution Loading", Quantum Reports 4 1, 75 (2022).
[18] Wenyang Qian, Robert Basili, Soham Pal, Glenn Luecke, and James P. Vary, "Solving hadron structures using the basis light-front quantization approach on quantum computers", Physical Review Research 4 4, 043193 (2022).
[19] Takashi Tsuchimochi, Yoohee Ryo, Seiichiro L. Ten-no, and Kazuki Sasasako, "Improved Algorithms of Quantum Imaginary Time Evolution for Ground and Excited States of Molecular Systems", Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 19 2, 503 (2023).
[20] Michele Grossi, Oriel Kiss, Francesco De Luca, Carlo Zollo, Ian Gremese, and Antonio Mandarino, "Finite-size criticality in fully connected spin models on superconducting quantum hardware", Physical Review E 107 2, 024113 (2023).
[21] Oriel Kiss, Michele Grossi, Pavel Lougovski, Federico Sanchez, Sofia Vallecorsa, and Thomas Papenbrock, "Quantum computing of the Li6 nucleus via ordered unitary coupled clusters", Physical Review C 106 3, 034325 (2022).
[22] Zhu Cao, "Deep Ising Born Machine", Advanced Quantum Technologies 6 7, 2300033 (2023).
[23] Erik Lötstedt, Takanori Nishi, and Kaoru Yamanouchi, Advances In Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics 73, 33 (2024) ISBN:9780443314582.
[24] Massimiliano Incudini, Fabio Tarocco, Riccardo Mengoni, Alessandra Di Pierro, and Antonio Mandarino, "Computing graph edit distance on quantum devices", Quantum Machine Intelligence 4 2, 24 (2022).
[25] Seyed Mohammad Hosseiny, Hossein Rangani Jahromi, and Mahdi Amniat-Talab, "Monitoring variations of refractive index via Hilbert–Schmidt speed and applying this phenomenon to improve quantum metrology", Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics 56 17, 175402 (2023).
[26] Alistair W R Smith, A J Paige, and M S Kim, "Faster variational quantum algorithms with quantum kernel-based surrogate models", Quantum Science and Technology 8 4, 045016 (2023).
[27] Werner Dobrautz, Igor O. Sokolov, Ke Liao, Pablo López Ríos, Martin Rahm, Ali Alavi, and Ivano Tavernelli, "Toward Real Chemical Accuracy on Current Quantum Hardware Through the Transcorrelated Method", Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 20 10, 4146 (2024).
[28] Ilya Piatrenka and Marian Rusek, Lecture Notes in Computer Science 13353, 247 (2022) ISBN:978-3-031-08759-2.
[29] Guglielmo Mazzola, "Quantum computing for chemistry and physics applications from a Monte Carlo perspective", The Journal of Chemical Physics 160 1, 010901 (2024).
[30] Christa Zoufal, Ryan V. Mishmash, Nitin Sharma, Niraj Kumar, Aashish Sheshadri, Amol Deshmukh, Noelle Ibrahim, Julien Gacon, and Stefan Woerner, "Variational quantum algorithm for unconstrained black box binary optimization: Application to feature selection", Quantum 7, 909 (2023).
[31] Enrico Rinaldi, Xizhi Han, Mohammad Hassan, Yuan Feng, Franco Nori, Michael McGuigan, and Masanori Hanada, "Matrix-Model Simulations Using Quantum Computing, Deep Learning, and Lattice Monte Carlo", PRX Quantum 3 1, 010324 (2022).
[32] Stefan H. Sack, Raimel A. Medina, Alexios A. Michailidis, Richard Kueng, and Maksym Serbyn, "Avoiding Barren Plateaus Using Classical Shadows", PRX Quantum 3 2, 020365 (2022).
[33] Marco Wiedmann, Marc Hölle, Maniraman Periyasamy, Nico Meyer, Christian Ufrecht, Daniel D. Scherer, Axel Plinge, and Christopher Mutschler, 2023 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE) 450 (2023) ISBN:979-8-3503-4323-6.
[34] Takanori Nishi and Kaoru Yamanouchi, "Simulation of a spin-boson model by iterative optimization of a parametrized quantum circuit", AVS Quantum Science 6 2, 023801 (2024).
[35] Alexander Mandl, Johanna Barzen, Marvin Bechtold, Frank Leymann, and Karoline Wild, "Amplitude amplification-inspired QAOA: improving the success probability for solving 3SAT", Quantum Science and Technology 9 1, 015028 (2024).
[36] Mazen Ali and Matthias Kabel, "Performance Study of Variational Quantum Algorithms for Solving the Poisson Equation on a Quantum Computer", Physical Review Applied 20 1, 014054 (2023).
[37] J. Cortés-Vega, J. F. Barra, L. Pereira, and A. Delgado, "Detecting entanglement of unknown states by violating the Clauser–Horne–Shimony–Holt inequality", Quantum Information Processing 22 5, 203 (2023).
[38] Almudena Carrera Vazquez, Daniel J. Egger, David Ochsner, and Stefan Woerner, "Well-conditioned multi-product formulas for hardware-friendly Hamiltonian simulation", Quantum 7, 1067 (2023).
[39] David Fitzek, Robert S. Jonsson, Werner Dobrautz, and Christian Schäfer, "Optimizing Variational Quantum Algorithms with qBang: Efficiently Interweaving Metric and Momentum to Navigate Flat Energy Landscapes", Quantum 8, 1313 (2024).
[40] Tobias Haug and M. S. Kim, "Natural parametrized quantum circuit", Physical Review A 106 5, 052611 (2022).
[41] Nishant Jain, Brian Coyle, Elham Kashefi, and Niraj Kumar, "Graph neural network initialisation of quantum approximate optimisation", Quantum 6, 861 (2022).
[42] Rafael Pereira da Silva, "Hamiltonian Minimization in the NISQ Era", SSRN Electronic Journal (2023).
[43] Johannes Jakob Meyer, "Fisher Information in Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum Applications", Quantum 5, 539 (2021).
[44] Martin Larocca, Nathan Ju, Diego García-Martín, Patrick J. Coles, and M. Cerezo, "Theory of overparametrization in quantum neural networks", arXiv:2109.11676, (2021).
[45] Tobias Haug, Kishor Bharti, and M. S. Kim, "Capacity and Quantum Geometry of Parametrized Quantum Circuits", PRX Quantum 2 4, 040309 (2021).
[46] Tobias Haug and M. S. Kim, "Optimal training of variational quantum algorithms without barren plateaus", arXiv:2104.14543, (2021).
[47] Yuxuan Du, Min-Hsiu Hsieh, Tongliang Liu, Shan You, and Dacheng Tao, "Learnability of Quantum Neural Networks", PRX Quantum 2 4, 040337 (2021).
[48] Christa Zoufal, "Generative Quantum Machine Learning", arXiv:2111.12738, (2021).
[49] Brian Coyle, "Machine learning applications for noisy intermediate-scale quantum computers", arXiv:2205.09414, (2022).
[50] Mirko Consiglio, "Variational Quantum Algorithms for Gibbs State Preparation", arXiv:2305.17713, (2023).
[51] Julien Gacon, Christa Zoufal, Giuseppe Carleo, and Stefan Woerner, "Stochastic Approximation of Variational Quantum Imaginary Time Evolution", arXiv:2305.07059, (2023).
[52] Anna Lopatnikova and Minh-Ngoc Tran, "Quantum Speedup of Natural Gradient for Variational Bayes", arXiv:2106.05807, (2021).
[53] Samantha V. Barron, Daniel J. Egger, Elijah Pelofske, Andreas Bärtschi, Stephan Eidenbenz, Matthis Lehmkuehler, and Stefan Woerner, "Provable bounds for noise-free expectation values computed from noisy samples", arXiv:2312.00733, (2023).
[54] Julien Gacon, "Scalable Quantum Algorithms for Noisy Quantum Computers", arXiv:2403.00940, (2024).
[55] Lucas Tecot and Cho-Jui Hsieh, "Randomized Benchmarking of Local Zeroth-Order Optimizers for Variational Quantum Systems", arXiv:2310.09468, (2023).
The above citations are from Crossref's cited-by service (last updated successfully 2024-07-04 14:35:04) and SAO/NASA ADS (last updated successfully 2024-07-04 14:35:05). The list may be incomplete as not all publishers provide suitable and complete citation data.
This Paper is published in Quantum under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. Copyright remains with the original copyright holders such as the authors or their institutions.