Quantum Interference of Force
Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Caixa Postal 701, 30161-970, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil
| Published: | 2018-12-14, volume 2, page 112 |
| Eprint: | arXiv:1802.10370v3 |
| Doi: | https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2018-12-14-112 |
| Citation: | Quantum 2, 112 (2018). |
Find this paper interesting or want to discuss? Scite or leave a comment on SciRate.
Abstract
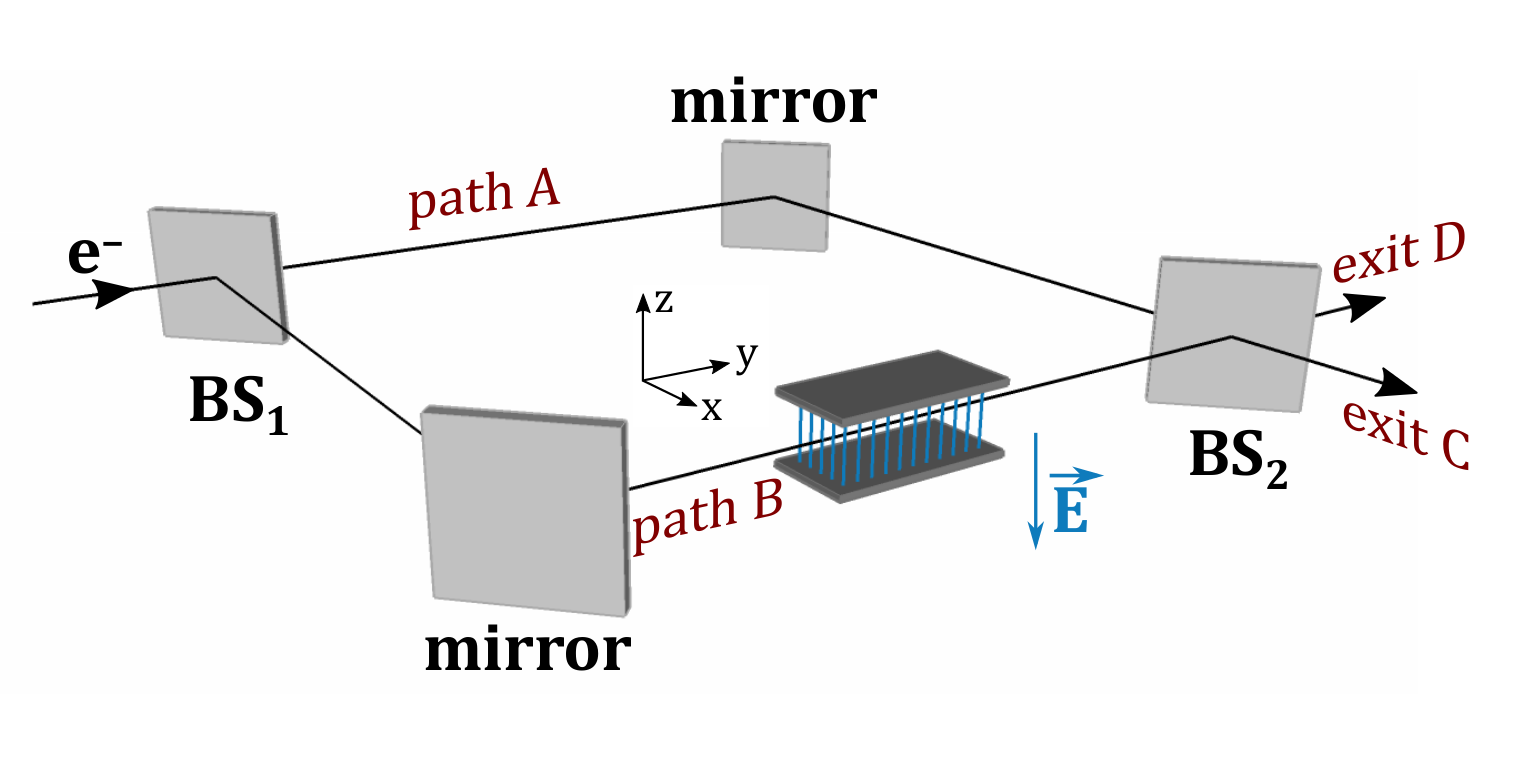
We show that a quantum particle subjected to a positive force in one path of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer and a null force in the other path may receive a negative average momentum transfer when it leaves the interferometer by a particular exit. In this scenario, an ensemble of particles may receive an average momentum in the opposite direction of the applied force due to quantum interference, a behavior with no classical analogue. We discuss some experimental schemes that could verify the effect with current technology, with electrons or neutrons in Mach-Zehnder interferometers in free space and with atoms from a Bose-Einstein condensate.
Popular summary
► BibTeX data
► References
[1] R. P. Feynman, R. B. Leighton, and M. Sands, The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Vol. III (Basic Books, New York, 2010).
[2] A. Tonomura, J. Endo, T. Matsuda, T. Kawasaki, and H. Ezawa, Am. J. Phys. 57, 117 (1989).
https://doi.org/10.1119/1.16104
[3] R. Bach, D. Pope, S.-H. Liou, and H. Batelaan, New J. Phys. 15, 033018 (2013).
https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/15/3/033018
[4] J. A. Wheeler, Mathematical foundations of quantum theory, edited by A. R. Marlow (Academic Press, 1978) Chap. The `past' and the `delayed-choice double-slit experiment', p. 9 to 48.
[5] V. Jacques, E. Wu, F. Grosshans, F. Treussart, P. Grangier, A. Aspect, and J.-F. Roch, Science 315, 966 (2007).
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1136303
[6] A. G. Manning, R. I. Khakimov, R. G. Dall, and A. G. Truscott, Nat. Phys. 11, 539 (2015).
https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3343
[7] F. Vedovato, C. Agnesi, M. Schiavon, D. Dequal, L. Calderaro, M. Tomasin, D. G. Marangon, A. Stanco, V. Luceri, G. Bianco, G. Vallone, and P. Villoresi, Sci. Adv. 3, 1701180 (2017).
https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1701180
[8] M. O. Scully, B.-G. Englert, and H. Walther, Nature 351, 111 (1991).
https://doi.org/10.1038/351111a0
[9] T. J. Herzog, P. G. Kwiat, H. Weinfurter, and A. Zeilinger, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3034 (1995).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.3034
[10] S. Durr, T. Nonn, and G. Rempe, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 5705 (1998).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.5705
[11] S. P. Walborn, M. O. Terra Cunha, S. Pádua, and C. H. Monken, Phys. Rev. A 65, 033818 (2002).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.65.033818
[12] A. C. Elitzur and L. Vaidman, Found. Phys. 23, 987 (1993).
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00736012
[13] P. Kwiat, H. Weinfurter, T. Herzog, A. Zeilinger, and M. A. Kasevich, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 4763 (1995).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.74.4763
[14] J. Peise, B. Lucke, L. Pezzé, F. Deuretzbacher, W. Ertmer, J. Arlt, A. Smerzi, L. Santos, and C. Klempt, Nat. Commun. 6, 6811 (2015).
https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7811
[15] R. Ionicioiu and D. R. Terno, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 230406 (2011).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.230406
[16] A. Peruzzo, P. Shadbolt, N. Brunner, S. Popescu, and J. L. O'Brien, Science 338, 634 (2012).
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1226719
[17] F. Kaiser, T. Coudreau, P. Milman, D. B. Ostrowsky, and S. Tanzilli, Science 338, 637 (2012).
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1226755
[18] Y. Aharonov, A. Botero, S. Nussinov, S. Popescu, J. Tollaksen, and L. Vaidman, New J. Phys. 15, 093006 (2013).
https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/15/9/093006
[19] Y. Aharonov, L. Davidovich, and N. Zagury, Phys. Rev. A 48, 1687 (1993).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.48.1687
[20] R. P. Feynman and A. R. Hibbs, Quantum mechanics and path integrals, Emended ed. (Dover, New York, 2010).
[21] C. Cohen-Tannoudji, B. Diu, and F. Laloe, Quantum Mechanics, 2nd ed. (Hermann by John Wiley & Sons, Paris, 1977).
[22] L. Marton, J. A. Simpson, and J. A. Suddeth, Rev. Sci. Instr. 25, 1099 (1954).
https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1770945
[23] H. Rauch, W. Treimer, and U. Bonse, Phys. Lett. A 47, 369 (1974).
https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9601(74)90132-7
[24] D. W. Keith, C. R. Ekstrom, Q. A. Turchette, and D. E. Pritchard, Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 2693 (1991).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.66.2693
[25] A. D. Cronin, J. Schmiedmayer, and D. E. Pritchard, Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1051 (2009).
https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.1051
[26] R. M. Godun, M. B. d'Arcy, G. S. Summy, and K. Burnett, Contemp. Phys. 42, 77 (2001).
https://doi.org/10.1080/00107510118044
[27] G. Gronniger, B. Barwick, and H. Batelaan, New J. Phys. 8, 224 (2006).
https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/8/10/224
[28] C. R. Ekstrom, J. Schmiedmayer, M. S. Chapman, T. D. Hammond, and D. E. Pritchard, Phys. Rev. A 51, 3883 (1995).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.51.3883
[29] T. D. Roberts, A. D. Cronin, M. V. Tiberg, and D. E. Pritchard, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 060405 (2004).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.060405
[30] A. Miffre, M. Jacquey, M. Buchner, G. Trénec, and J. Vigué, Phys. Rev. A 73, 011603(R) (2006).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.73.011603
[31] H. Rauch and S. Wener, Neutron interferometry, 2nd ed. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2015).
[32] Y. Hasegawa and H. Rauch, New J. Phys. 13, 115010 (2011).
https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/13/11/115010
[33] H. Geppert, T. Denkmayr, S. Sponar, H. Lemmel, and Y. Hasegawa, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 763, 417 (2014).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2014.06.080
[34] T. Denkmayr, H. Geppert, H. Lemmel, M. Waegell, J. Dressel, Y. Hasegawa, and S. Sponar, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 010402 (2017).
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.010402
[35] M. F. B. Cenni, R. Corrêa, and P. L. Saldanha, arXiv:1808.07082.
arXiv:1808.07082
Cited by
[1] Marina F. B. Cenni, Raul Corrêa, and Pablo L. Saldanha, "Effective electrostatic attraction between electrons due to quantum interference", Physical Review A 100 2, 022101 (2019).
[2] Raul Corrêa and Pablo L. Saldanha, "Apparent quantum paradoxes as simple interference: Quantum violation of the pigeonhole principle and exchange of properties between quantum particles", Physical Review A 104 1, 012212 (2021).
[3] M. S. Hosseini and S. A. Alavi, "Breit-Wigner distribution, quantum beats and GSI Anomaly", arXiv:1704.05762, (2017).
The above citations are from Crossref's cited-by service (last updated successfully 2024-07-26 18:08:58) and SAO/NASA ADS (last updated successfully 2024-07-26 18:08:59). The list may be incomplete as not all publishers provide suitable and complete citation data.
This Paper is published in Quantum under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. Copyright remains with the original copyright holders such as the authors or their institutions.